Low Testosterone in Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Low testosterone in men can lead to fatigue, depression, and decreased sex drive. It affects physical and mental health.
Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, occurs when the body produces insufficient testosterone. This hormone is crucial for male development and overall health. Symptoms include low energy, mood changes, and reduced muscle mass. Men may also experience erectile dysfunction and decreased libido.
These symptoms can impact daily life and relationships. Various factors, such as aging, obesity, and medical conditions, can contribute to low testosterone levels. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage symptoms effectively. Options include lifestyle changes, medications, and hormone replacement therapy. Consulting a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment is important for maintaining quality of life.
Introduction To Low Testosterone
Low testosterone affects many men. This condition can impact health and well-being. It’s important to understand its causes and effects.
What Is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a hormone. It is mainly produced in the testes. It plays a key role in male health. Both men and women have it, but men have more.
Importance Of Testosterone In Men
Testosterone is crucial for many bodily functions. It helps in muscle growth and bone density. It also affects mood and energy levels.
Here are some key functions of testosterone:
- Muscle mass development
- Bone strength
- Sex drive
- Sperm production
- Fat distribution
Low testosterone can lead to various health issues. It may cause fatigue, depression, and decreased libido. Recognizing the symptoms early is important.
Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial. They can diagnose and treat low testosterone effectively.

Credit: www.thrivelab.com
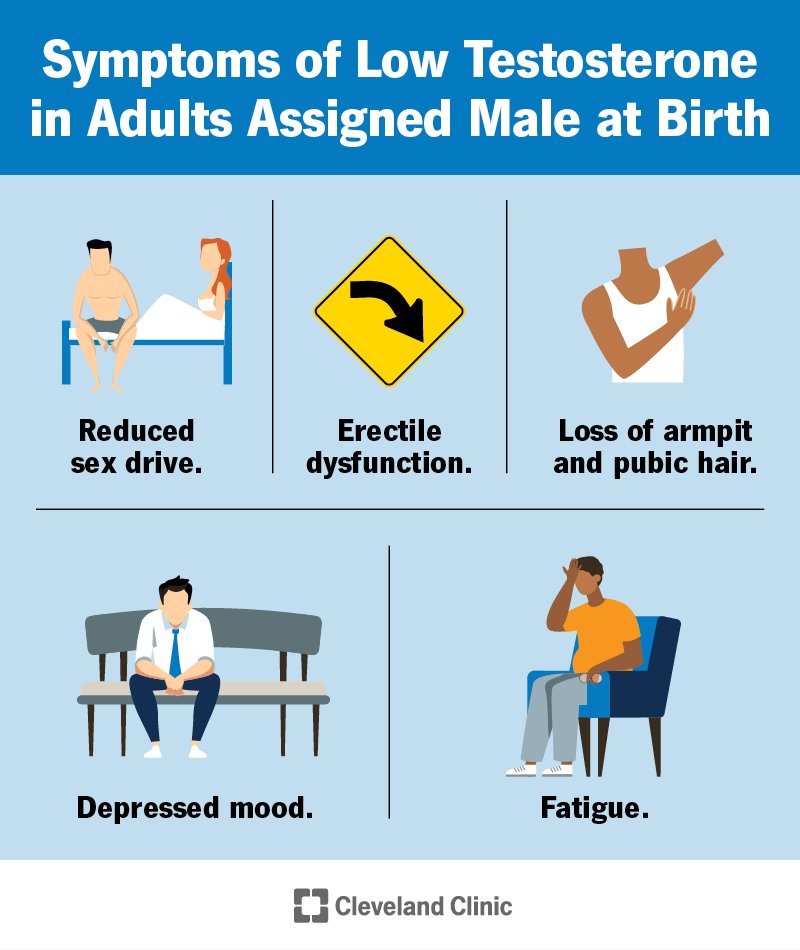
Common Symptoms
Low testosterone in men can lead to various symptoms. Understanding these symptoms is crucial. Below, we explore the most common symptoms divided into physical, emotional, and cognitive categories.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms are often the first signs of low testosterone. These symptoms can impact daily activities significantly.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness even after adequate rest.
- Muscle Loss: Reduced muscle mass and strength.
- Increased Body Fat: Noticeable weight gain, especially around the abdomen.
- Hair Loss: Thinning or loss of body and facial hair.
- Decreased Libido: Reduced interest in sexual activities.
Emotional Symptoms
Emotional symptoms can affect relationships and mental health. Men may experience mood changes and other emotional disturbances.
- Depression: Feeling sad or hopeless for extended periods.
- Anxiety: Increased feelings of worry or nervousness.
- Irritability: Short temper and frequent mood swings.
- Lack of Motivation: Reduced drive and enthusiasm for activities.
Cognitive Symptoms
Low testosterone can also impact cognitive functions. These symptoms might affect work performance and daily tasks.
- Memory Issues: Difficulty remembering things.
- Concentration Problems: Trouble focusing on tasks.
- Slower Thinking: Reduced ability to process information quickly.
Underlying Causes
Low testosterone in men can stem from various underlying causes. Understanding these causes can help in managing the condition better. Below are some significant factors that contribute to low testosterone levels in men.
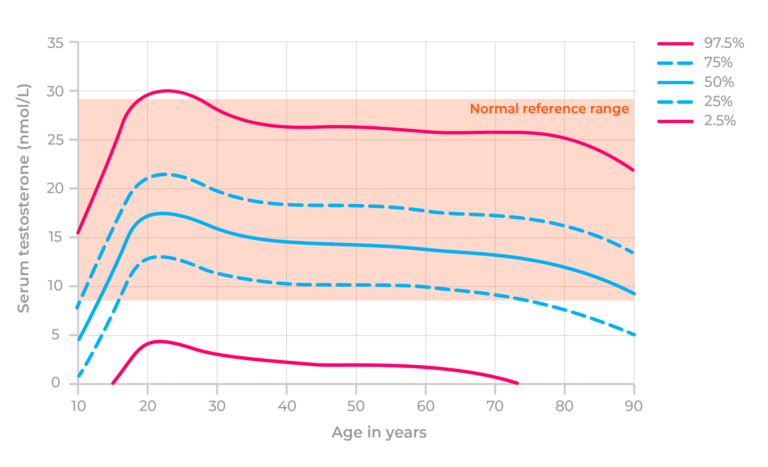
Age-related Decline
As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decrease. This decline usually starts after the age of 30. By the time men reach their 70s, their levels can be significantly lower. This natural decline is a major cause of low testosterone in older men.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can lead to low testosterone levels. Common conditions include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can affect hormone production.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can lower testosterone levels.
- Chronic Illnesses: Diseases like kidney failure and liver disease can impact hormone levels.
- Infections: Certain infections can damage the testicles, reducing testosterone production.
Each of these conditions can significantly impact testosterone levels in men.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in testosterone levels. Key factors include:
- Poor Diet: A diet low in essential nutrients can affect hormone production.
- Lack of Exercise: Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and lower testosterone.
- Stress: Chronic stress increases cortisol, which can reduce testosterone.
- Sleep Deprivation: Poor sleep quality can significantly impact testosterone levels.
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can help maintain normal testosterone levels.
Summary Table
| Cause | Details |
|---|---|
| Age-Related Decline | Natural decrease in testosterone as men age. |
| Medical Conditions | Diabetes, obesity, chronic illnesses, infections. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, sleep deprivation. |
Diagnosis Process
Low testosterone in men can impact life quality. It is essential to get a proper diagnosis. The diagnosis process involves several steps. Each step helps in understanding the condition better.
Medical History Review
The first step is the medical history review. Doctors ask about your symptoms. They need to know about your health history. They also ask about your family’s health. This helps to identify potential risk factors.
| Questions Asked | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Current Symptoms | Identify signs of low testosterone |
| Past Medical History | Understand underlying health issues |
| Family Health | Check for hereditary conditions |
Blood Tests
The next step is blood tests. Blood tests measure testosterone levels. Usually, the test is done in the morning. This is because testosterone levels are highest then.
- Fasting may be required before the test
- Several samples may be needed for accuracy
- Results help determine if levels are low
Additional Tests
Sometimes, doctors may recommend additional tests. These tests help to rule out other conditions. They also provide more information about your health.
- Hormone Tests: Check levels of other hormones like LH and FSH
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI to look at testicular structure
- Bone Density Test: Measures bone health and checks for osteoporosis
These steps ensure a thorough diagnosis. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Traditional Treatments
Low testosterone in men can lead to many health issues. Traditional treatments are effective in managing this condition. These treatments include hormone replacement therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a common treatment for low testosterone. HRT helps restore testosterone levels in men. This can improve energy, mood, and sexual function.
There are several methods for HRT:
- Injections
- Skin patches
- Gels
- Implants
Each method has its pros and cons. Your doctor will recommend the best option for you.
Medications
Medications are another option for treating low testosterone. These drugs can stimulate the body to produce more testosterone.
Common medications include:
- Clomiphene Citrate
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- Anastrozole
These medications can be effective but may have side effects. Always consult your doctor before starting any medication.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can also help manage low testosterone. These changes often have fewer risks than medications or HRT.
Effective lifestyle changes include:
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Stress reduction
- Adequate sleep
These changes can improve overall health and boost testosterone levels.
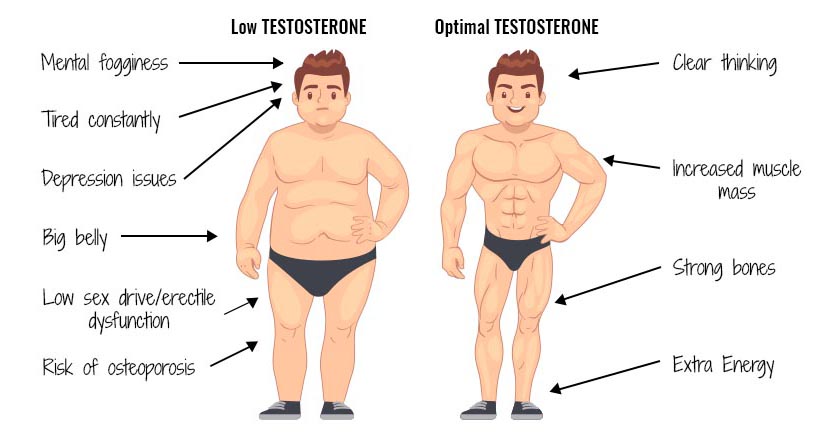
Credit: trtuk.co.uk
Natural Remedies
Low testosterone can impact a man’s health and well-being. Natural remedies offer a way to boost testosterone levels without medication. Focus on these key areas: dietary adjustments, exercise, and supplements.
Dietary Adjustments
Diet plays a crucial role in managing testosterone levels. Certain foods can help increase testosterone production:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, and turkey support muscle growth and testosterone.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil boost hormone levels.
- Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are rich in vitamins.
Avoid processed foods and excess sugar. These can lower testosterone and harm health. Stay hydrated and limit alcohol intake.
Exercise
Exercise is vital for maintaining healthy testosterone levels. Focus on strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT):
- Strength Training: Lifting weights helps increase testosterone.
- HIIT: Short bursts of intense exercise boost hormone production.
- Cardio: Running or cycling improves overall health.
Consistency is key. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise, five days a week.
Supplements
Supplements can support natural testosterone production. Consider these options:
| Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Zinc | Boosts testosterone and immune function. |
| Vitamin D | Supports hormone balance and overall health. |
| Magnesium | Improves muscle function and testosterone levels. |
| Ashwagandha | Reduces stress and increases testosterone. |
Consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement. Ensure you choose high-quality products for best results.
Potential Risks
Low testosterone levels in men can lead to significant health risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for managing and preventing complications. This section explores the side effects of treatments and long-term health implications associated with low testosterone.
Side Effects Of Treatments
Many men opt for testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) to combat low testosterone levels. While TRT can be effective, it also has side effects:
- Acne and oily skin: Increased testosterone can lead to skin issues.
- Sleep apnea: TRT may worsen this sleep disorder.
- Heart problems: Some studies suggest a link to cardiovascular issues.
- Prostate growth: TRT can stimulate prostate tissue, leading to issues.
- Blood clots: Higher testosterone levels may increase clot risks.
Long-term Health Implications
Low testosterone can affect long-term health in various ways:
| Health Aspect | Implication |
|---|---|
| Bone Density | Men with low testosterone may have weaker bones. |
| Heart Health | Low testosterone levels are linked to heart disease. |
| Mental Health | Men may experience depression and mood swings. |
| Muscle Mass | Low testosterone can lead to muscle loss. |
| Fat Distribution | Men may gain weight, especially around the abdomen. |
Understanding these risks can help manage low testosterone effectively. Early intervention and proper treatment are key to mitigating these health concerns.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Low-testosterone-5216619_txt_final-f54332d26a124869bb49e110d5d09d2f.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Living With Low Testosterone
Living with low testosterone can be challenging for many men. It affects both physical and emotional well-being. Understanding how to manage symptoms and find support is crucial.
Managing Symptoms
There are many symptoms of low testosterone in men. These include fatigue, depression, and reduced muscle mass. Below are some ways to manage these symptoms:
- Regular Exercise: Helps boost energy levels and improve mood.
- Healthy Diet: Eating balanced meals supports hormone health.
- Medication: Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be an option.
Support Systems
Having a support system is vital for living with low testosterone. Family and friends can provide emotional support. Joining a support group can also be beneficial. You can share experiences and learn from others.
Consider talking to a therapist. They can help you manage the emotional impact of low testosterone.
Future Outlook
Research on low testosterone is ongoing. New treatments and therapies are being developed. Staying informed can help you make the best decisions for your health.
Here are some ways to stay updated:
- Follow medical news websites.
- Join online forums related to low testosterone.
- Talk to your doctor about the latest research.
With the right management and support, living with low testosterone can become easier.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens If A Man’s Testosterone Is Low?
Low testosterone can cause fatigue, depression, reduced muscle mass, and decreased libido. It may also lead to weight gain and mood swings.
How Do I Fix My Low Testosterone?
Consult a doctor for hormone replacement therapy. Improve diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Reduce stress and avoid alcohol.
How Can I Raise My Testosterone Level?
Boost testosterone by exercising regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, reducing stress, and taking vitamin D.
Can You Live A Normal Life With Low Testosterone?
Yes, you can live a normal life with low testosterone. Treatment options and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
Low testosterone in men affects physical health, mood, and energy levels. Addressing it early can improve quality of life. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can also help. Understanding symptoms and treatments empowers men to take control of their health.